小优智能科技有限公司成立于2015年底,是一家专注于高精度3D机器视觉模组研发、生产及销售的高科技企业。
公司自主研发的3D机器视觉模组采用激光/DLP白光编码光栅结构光+双工业相机方案,还原物体三维信息,广泛应用于消费电子领域、工业领域和安防领域,具有精度高、速度快、成本低的优势。
In a 3D robotic vision workflow, 3D cameras are often an essential step to facilitate object modeling. They
can collect shape data and, sometimes depending on the 3D scanner, appearance (e.g., color) data. 3D
scanning, therefore, enhances the design process, speeds up and reduces errors in data collection, and
can also save time and money.
3D scanning can be based on different technologies, each with its own advantages and limitations. In this
article, we explore the two main technologies used for 3D robotic vision cameras, laser triangulation and
structured light cameras. So, how do laser cameras compare to structured light cameras? And most import
antly, which one should you choose for your project?
Laser cameras: technology, advantages and limitations
Laser cameras are based on triangulation and can capture 3D shapes with great accuracy (millions of
points). More precisely, they work by projecting a laser dot or line onto an object and capturing its
reflection with a sensor. Since the sensor is located at a known distance from the laser source, precise
point measurements can be made by calculating the reflection angle of the laser. With the knowledge of
the scanner-to-object distance, the scanning hardware can map the surface of the object and thus record
a 3D scan.
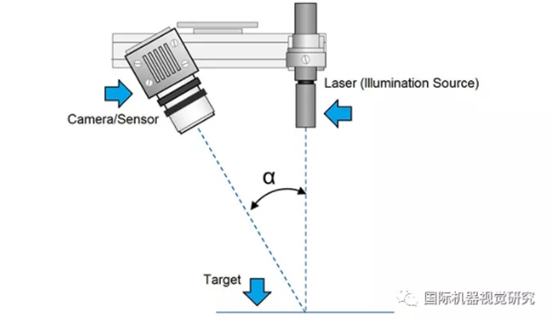
This method is called triangulation, because the laser dot (or line), sensor and laser emitter form a triangle,
as shown in the figure below. There are many different types of laser scanners on the market, and you
can choose between handheld, desktop or professional/industrial devices. The key is that they can work
at short distances. Lasers also have the strong advantage of directing strong light in a narrow range of
wavelengths, so they work well and stably in almost any environment.
The strength of laser triangulation technology lies in its resolution and accuracy. When it comes to
accuracy, it is on the order of tens of microns. However, you should be aware that the properties of the
surface to be scanned can affect the scanning process. Therefore, very glossy or transparent surfaces
may be problematic for this technology.
Structured light cameras: technology, advantages and limitations
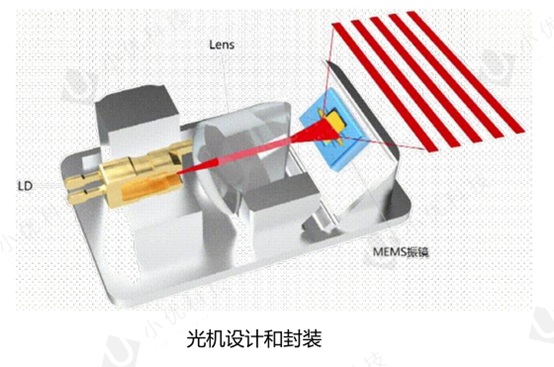
Today, many handheld 3D scanners for 3D cameras use structured light technology. This technology also uses triangulation, but works by projecting a pattern of light onto the object to be scanned instead of a laser line (or point). The dynamic structured light 3D camera developed by Xiaoyou Intelligent projects a pattern onto the object, and one or more sensors (or cameras) are slightly offset from the projector. They observe the shape of the light pattern and calculate the distance of each point in the field of view. The light pattern is usually composed of a series of stripes.
The benefit of structured light technology is that it scans quickly. It can be done in about 0.2 seconds, and
the scan area is also large. Just like laser scanners, structured light scanners are also very accurate and
have high resolution.
One of the disadvantages of structured light cameras is that they are sensitive to the lighting conditions
in a given environment.